Service hotline
+86 0755-83044319
release time:2022-03-17Author source:SlkorBrowse:13774
Since 2020, the global wafer foundry output value has entered a state of vigorous development. It can be seen from Figure 1 that its annual growth rate has reached 24%. The annual growth rate in 2021 will reach 22.4%, which is also a high level of growth. This year, the output value of the entire wafer foundry will officially exceed the $100 billion mark. TrendForce predicts that the annual growth rate in 2022 will be 13.3%. There are two keys to driving the growth again in 2022, one is the newly opened production capacity, and the other is the price increase.
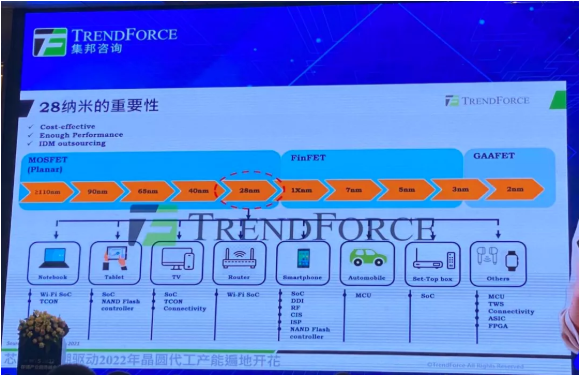
Figure 1: Estimated global output value of foundry
In 2021, various fabs have launched plans to expand production. In 2022, it is expected that there will be 12 new wafer foundries (see Figure 2). Among them, [敏感词], China, driven by [敏感词], the entire wafer foundry. From the perspective of output value, [敏感词]'s output value is about 60%, and production capacity accounts for 50%, which means that most of the relatively expensive advanced manufacturing processes are still in [敏感词]. made in the region. There is another point worth paying attention to. It can be seen from Figure 2 that in 2022, the foundry market share in [敏感词] seems to drop slightly by 1%, and mainland China will increase by 2%. Most of the increased production capacity is concentrated in the Nanjing plant in mainland China. However, [敏感词]'s focus is still on [敏感词].
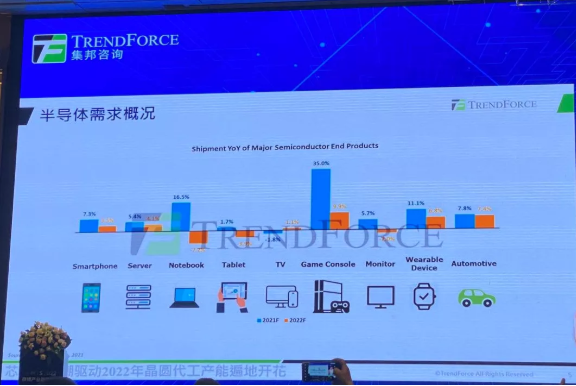
Figure 2: Major foundry new fab locations
In terms of advanced process, everyone is more concerned about the 3nm process launched by [敏感词] and Samsung. [敏感词] still uses the FinFEX architecture. The 3nm products released by Samsung are based on the GAA architecture, which is also the only company in the industry that has imported this architecture. [敏感词] accounts for nearly 70% of the advanced process market, and Samsung accounts for about 30%. Most of these two companies' expansion plans this year are still concentrated in the 5nm and 4nm parts. Next year, these two companies will be concentrated. in the 3nm process.
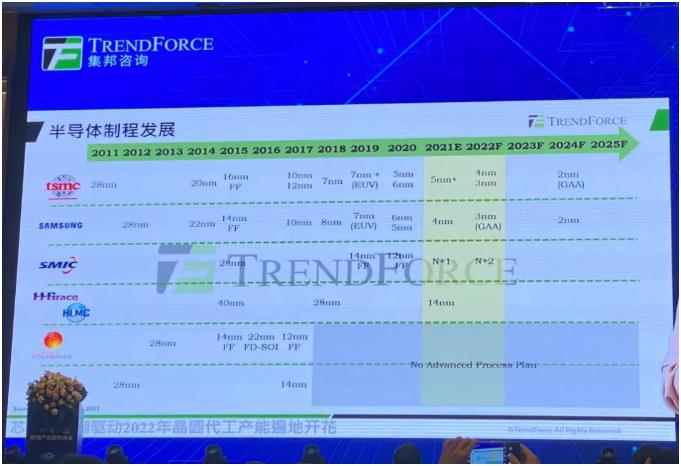
Figure 3: Semiconductor process development
Foundry capacity is fully loaded, 8-inch wafers will be tighter than 12-inch wafers in 2022
In 2021, the capacity utilization rate of both 8-inch and 12-inch foundries is as high as 95-100%, and this sign will continue into 2022.
According to the data shared by TRENDFORCE, the 12-inch wafer foundries listed [敏感词], Samsung, UMC, and SMIC. From the dotted line in Figure 4, it can be seen that there will be a slight downward trend in the second half of 2022. , Qiao An said, in fact, this is not a bad demand, the main reason is that there are some new production capacity or new factories start to open production capacity one after another, and the denominator becomes larger when the filming volume does not keep up quickly. , the utilization rate will drop a little bit, and we currently believe that the entire utilization rate will remain above 95%.
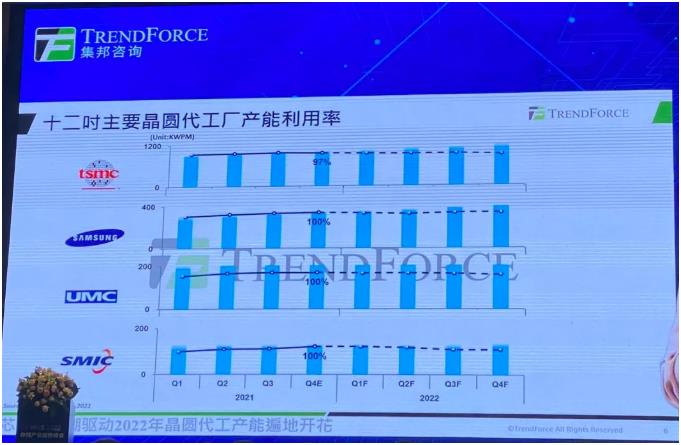
Figure 4: 12-inch major foundry capacity utilization
From Figure 5, the decline in 8-inch foundry capacity is not so obvious, mainly because the growth rate of 8-inch capacity is relatively limited, demand growth is greater than supply, and the tight situation will be more severe than 12-inch. On the demand side, most of the power management-related ICs used in 5G mobile phones and electric vehicles are manufactured in 8-inch factories, but most of the equipment in 8-inch wafer foundries are more expensive, but 8-inch wafers are expensive. The price of 8-inch fabs is relatively cheap, resulting in the expansion of 8-inch fabs that are not cost-effective. On the contrary, driven by the booming demand, the 8-inch capacity shortage is more serious than that of 12-inch fabs.
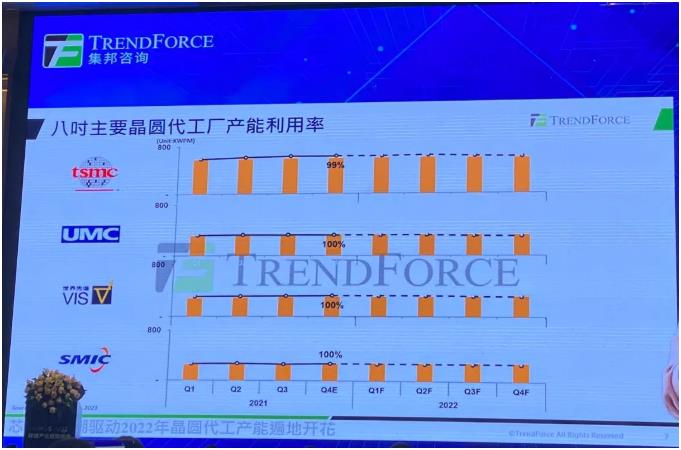
Figure 5: 8-inch major foundry capacity utilization
It is obvious from Figure 6 that the 5-year compound annual growth rate of 8-inch wafer capacity is only 3%, and the slope of its annual growth rate is significantly smaller than that of 12-inch fabs. 12 inches is tight. Driven by shortages, the 12-inch plant has seen an annual growth rate of 12%. It is understood that from 2021 to 2023, 100K to 200K of new production capacity will be opened every year.
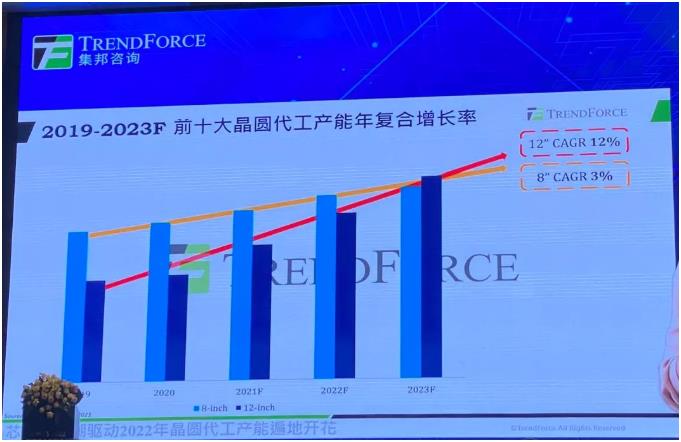
Figure 6: 2019-2023F CAGR of top 10 foundry capacity
2022 process capacity expansion plan: 40nm and 28nm are the key points
Qiao An pointed out, "In 2021, in the capacity expansion plan of each process, most of the new products are concentrated in the 90nm, 65nm or 55nm part, and the new production capacity is up to 80K, but the reason for the continued tightness this year is that 90nm, 65nm, 55nm The products that can be produced may be slightly relieved, and the focus is on 40nm or 28nm. For example, Wi-Fi products focused on the 40nm and 28nm processes are still in a tight state.”

Figure 7: 2021F Capacity Expansion Plan for Each Process
"But looking at 2022, in the red box, the new production capacity next year will be mainly concentrated in the 40nm and 28nm parts, so we believe that the opening of these new production capacity next year will bring about a shortage of wafer foundry market conditions. Come for some soothing signs."
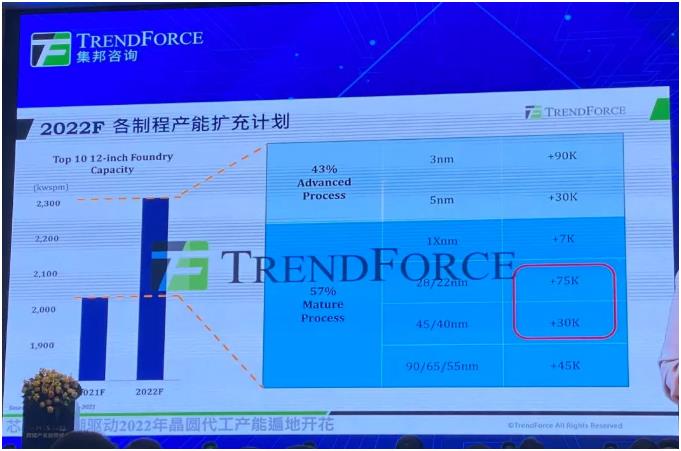
Figure 8: 2022F capacity expansion plan for each process
90nm, 65nm and 55nm are the main capacity expansions this year, and 40nm and 28nm are the main support for next year's expansion. Therefore, it can be understood that the current supplier of 1Xnm is very few. After entering 1Xnm, the transistor structure has entered the FinFEX structure, so the cost of expansion is relatively high. Currently, only [敏感词], Samsung and other companies have no plans to expand production in the next few years. As the penetration rate of 5G mobile phones increases year by year, the demand for 1Xnm chips will also increase a lot, and the demand for Wi-Fi, etc. is also growing year by year, which may cause the bottleneck process of 1Xnm in 2022 and 2023.
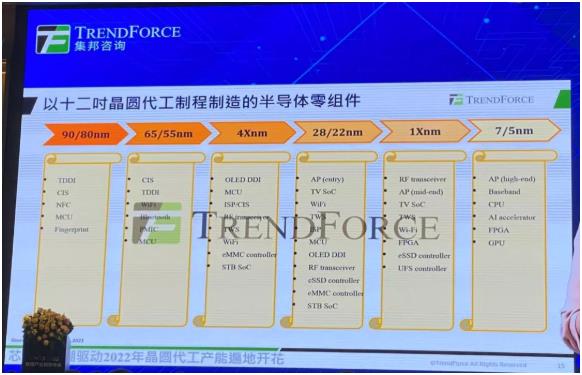
Figure 9: Semiconductor components fabricated on a 12-inch foundry process
Why is the 28nm process so important?
Qiao An pointed out that not only next year, but even after 2023, the production capacity of 28nm will be gradually increased. Why is the 28nm process so important?
As can be seen from Figure 10, 28nm is the most advanced process under the MOSFET (Planar) architecture. Compared with the FinFET architecture, that is, after 1Xnm, the cost is relatively cheap. 28nm is in the last generation of MOSFET (Planar) architecture, which can provide sufficient performance of chips required for a large number of IoT products.
In addition, when entering below 40nm, when most wafer foundries or IDM factories are expanding production, the cost is also relatively large. If they do not have enough customers to support the operation of these factories, it is likely to cause Losses, so after entering below 40nm, many IDM factories have successively outsourced some products to these wafer foundries for manufacturing. As a result, most wafer foundries actively want to expand the production capacity of 40nm/28nm.

Figure 10: The Importance of 28nm
Will 2022 be the end of the chip shortage?
According to data from TRENDFORCE, the market demand for semiconductor end products in 2020 will be strong. As can be seen from Figure 4, in addition to TV, which experienced a negative growth of 1.8%, game consoles, notebooks, wearable devices, automobiles, monitors, servers, Smartphones are showing rapid growth. In fact, the main driving force is that the new crown epidemic has driven various demands, especially the positive growth of game consoles, notebooks, and wearable devices as high as 35%, 16.5%, and 11.1%. In 2022, this epidemic-related demand will enter a weak state. Qiao An, an analyst at TrendForce’s Semiconductor Research Department, pointed out that it is worth noting that “changes in product mix” are one of the key drivers for the development of semiconductor demand, such as 4G mobile phones to 5G mobile phones, traditional cars to electric vehicles and other products Combination changes, product mix changes will double the number of chips used, for example, a larger size TV requires a higher resolution, which requires more chips.

Figure 11: Overview of Semiconductor Demand
Qiao An, an analyst at the Semiconductor Research Department of TrendForce, said that the main reason for the shortage of chips is the penetration rate of 5G mobile phones, which has continued to develop since the second half of 2019. After entering 2020, it happened to encounter the new crown epidemic and geopolitics. and other related factors, these three factors actually bring about two same results, one is the increase in product demand, and the second is the uncertainty caused by geopolitics or the epidemic, such as the closure of the city and the country. And so on, causing the supply chain to break. Therefore, the stocking kinetic energy of the entire supply chain will be disrupted, and most supply chains will need to establish a relatively high inventory level in order to cope with the problem of out-of-stocks caused by the closure of the city and the country or geopolitics, which is the large-scale shortage of goods. main reason.
When will we see the end of the chip shortage wave? Most of the products this year are concentrated in 96nm and 65nm, and next year will form the expansion of 40nm and 28nm. These processes will appear in the supply relaxation situation this year and next year. However, the increase in the capacity of 8-inch wafers is slightly limited. In addition, there are relatively few 1Xnm suppliers, and there is currently no clear expansion plan. 8-inch and 5Xnm, and 12nm, 16nm, or 11nm, 14nm , may become the bottleneck process next year. Therefore, we are currently observing that in 2022 as a whole, although the wafer foundries continue to open up new production capacity in some processes, there may be some signs of a little relief, but the 8-inch and 1Xnm bottleneck processes will still be The entire semiconductor supply chain will continue to have a problem of long and short materials. Therefore, from the perspective of the entire wafer foundry market, there will still be a situation of tight production capacity in 2022.
Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from " Electronic Engineering Album Author: Wu Qingzhen Amy Wu", this article only represents the author's personal views, not Sacco Micro and the industry's views, only for reprinting and sharing, to support the protection of intellectual property rights, please reprint Indicate the original source and author. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it.



Site Map | 萨科微 | 金航标 | Slkor | Kinghelm
RU | FR | DE | IT | ES | PT | JA | KO | AR | TR | TH | MS | VI | MG | FA | ZH-TW | HR | BG | SD| GD | SN | SM | PS | LB | KY | KU | HAW | CO | AM | UZ | TG | SU | ST | ML | KK | NY | ZU | YO | TE | TA | SO| PA| NE | MN | MI | LA | LO | KM | KN
| JW | IG | HMN | HA | EO | CEB | BS | BN | UR | HT | KA | EU | AZ | HY | YI |MK | IS | BE | CY | GA | SW | SV | AF | FA | TR | TH | MT | HU | GL | ET | NL | DA | CS | FI | EL | HI | NO | PL | RO | CA | TL | IW | LV | ID | LT | SR | SQ | SL | UK
Copyright ©2015-2025 Shenzhen Slkor Micro Semicon Co., Ltd