Service hotline
+86 0755-83044319
release time:2022-03-17Author source:SlkorBrowse:12039
Since the second half of 2020, component shortages and price increases have become the main theme of the market. The lack of cores even affects the normal operation of the downstream terminal market, resulting in a serious production reduction in the automotive industry. The concentrated outbreak of downstream demand after the epidemic is the trigger for this round of shortages and price increases. The panic stocking of the industrial chain caused by the uncertainty of Sino-US relations has partially amplified the elasticity of demand.
The surge in the global semiconductor industry is followed by the shortage of goods and price increases. In January 2021, the sales growth rate of the global semiconductor industry is as high as 13.2% year-on-year. ICInsights predicts that the global semiconductor market growth rate is expected to reach 19% in 21 years.
So when will this out-of-stock price rise begin and when will it end? What profound impact will it have on our entire supply chain?
A story about "jumping"

The article begins with a story about "jumping off a building".
In August of this year, David Xu, vice president of Bosch China, explained in a circle of friends that the recent shortage of stock or supply has caused a supply cut, and a piece of white paper said "Sixth floor. To jump or not to jump? To bring a leader or not to bring "The text reveals "despair" everywhere.
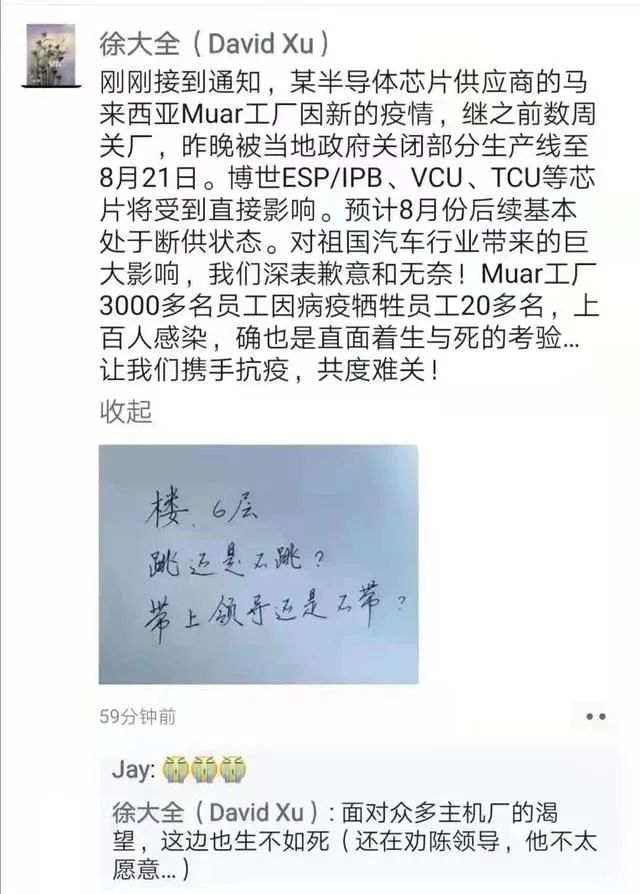
According to Xu Daquan, a semiconductor chip supplier's Muar factory in Malaysia was affected by the new wave of the new crown epidemic. Hundreds of more than 3,000 employees in the Muar factory were infected with the epidemic, and more than 20 people died due to the epidemic. Following the closure of the factory in the previous weeks, the local government closed some product lines of Bosch until August 21. This move will directly affect the production of Bosch ESP/IPB, VCU, TCU and other chips. It is expected that the supply will be basically cut off in August. He said that he is very sorry and helpless for the huge impact on the auto industry of the motherland.
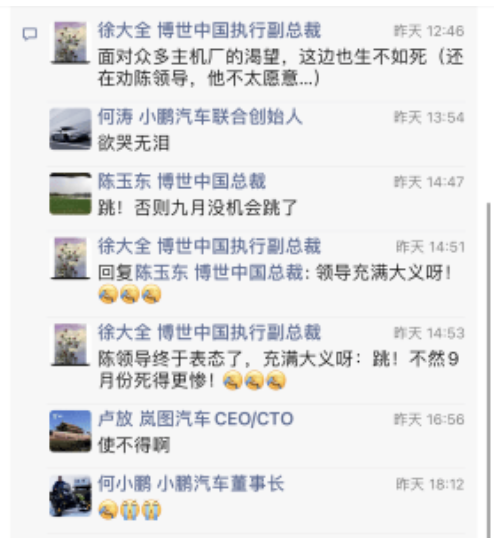
In the comment area below, Bosch China President Chen Yudong replied jokingly: "Jump! Otherwise, there will be no chance to jump in September." Xu Daquan also jokingly said that the leader was right. Car executives were also "horrified" and commented in the comment section.
2021 price hike review
Since the beginning of this year, many semiconductor manufacturers have issued price increase letters.
ADI stated in the price increase letter that after the merger of ADI and Maxim, Maxim's products will maintain the original 6% increase, and some ADI products will also be increased, and the price increase will officially take effect on December 5. The main reason for the price increase is the rising price of raw materials, especially wafers.
SiliconLabs said that the crisis in the semiconductor supply chain has seriously affected, and SiliconLabs not only strives to meet the current production capacity needs of customers, but also needs to expand production capacity to meet long-term needs. With the increase in the cost of raw materials, wafers, packaging and testing, logistics, labor, etc., SiliconLabs will officially increase the price from November 28, and unshipped orders will also be executed at the latest price.
Toshiba recently issued a price increase letter in English. The price increase letter shows that its optocoupler will officially increase the price in January 2022.
WiFi chip manufacturers such as MediaTek and Realtek said they would increase by another 10%. In addition, a number of major manufacturers announced that they will rise in the first quarter of 2022:
The tide of price increases due to lack of cores is getting more and more intense, and the price increases are first from wafer foundry, packaging and testing, and then transferred to chips and even end products. The earliest wafer foundries such as UMC, GF and World Advanced raised their quotations by about 10%-15% for urgent 8-inch foundry orders and new production orders, and prices have continued to rise since then. In 21 years, the tide of price increases has spread from 8 inches to 12 inches.
Due to the shortage of wafer foundry capacity and the heating up of the new crown epidemic, the shortage of the global semiconductor supply chain has intensified, and the shortage of chips may continue to 2023-2024. In addition to canceling the discounts given to customers in previous years (disguised price increases), [敏感词] also announced a price increase: mature processes will increase by 10-20%, advanced processes will also increase by 10%, and prices will be increased in 2022. Effective in the first quarter. It is reported that this round of raising the mature process is mainly aimed at 16nm and above, and the advanced process is aimed at 7nm and more advanced processes.
UMC will launch a new wave of price increases, mainly targeting the three major US-based customers who account for more than 30% of their revenue, with an increase of about 8% to 12%. It will take effect from January 2022. UMC's current major customers in the United States include major manufacturers such as AMD, Qualcomm, Texas Instruments, and Nvidia, and hold orders from European manufacturers such as Infineon and STMicroelectronics.
KeyFoundry and Samsung also said that foundry prices will increase by 15% to 20%, and the new prices will take effect in 4 to 5 months.
The price increase of PSMC in the first quarter of 2022 is estimated to exceed 10%, and it is expected to increase every six months. Huang Chongren, chairman of RSMC, also made it clear to the outside world recently that he is talking to customers about orders in 2023, and the price increase is a general trend. As long as the customer's gross profit margin exceeds that of RSMC, it will increase. The world's advanced and other industries will follow up with price increases in the first quarter, with an average increase of more than 10%.
Since the industry is optimistic that the chip shortage problem will continue after 2023 after the epidemic slows down and the economy is unblocked, more than half of customers choose to sign long-term contracts of 2 to 3 years. It is a foregone conclusion that the price of the wafer foundry will increase in the first quarter of 2022, and the price increase will be even higher if no long-term contract is signed.
The supply of packaging and testing terminals is also in short supply, and the wire-bonding packaging and flip-chip packaging are all in short supply. In the fourth quarter of 2020, ASE, the leader in IC packaging and testing, has raised about 20% to 30% of new packaging and testing orders and urgent orders in the fourth quarter. ~10% range. And the company expects at the performance briefing that the company's production capacity will remain fully loaded, and the shortage of wire bonding and packaging will continue until 2021.
The increase in the price of upstream production capacity has brought about the continuous delay in the delivery of the original semiconductor factory. The price increase and the shortage of stock are further transmitted to the end products, of which the automobile market is the most affected. A large number of MCUs, MOSFETs, IGBTs and other power semiconductors are used in automobiles. For example, under normal circumstances, the MCU delivery time is about 8 weeks, while the current delivery time of international manufacturers such as Infineon, NXP, and Renesas Electronics is generally as high as 24-52 week. Due to the shortage of chips, downstream OEMs such as Honda, Nissan, Toyota, Ford, Volkswagen, and General Motors have successively issued plans to stop or reduce production.
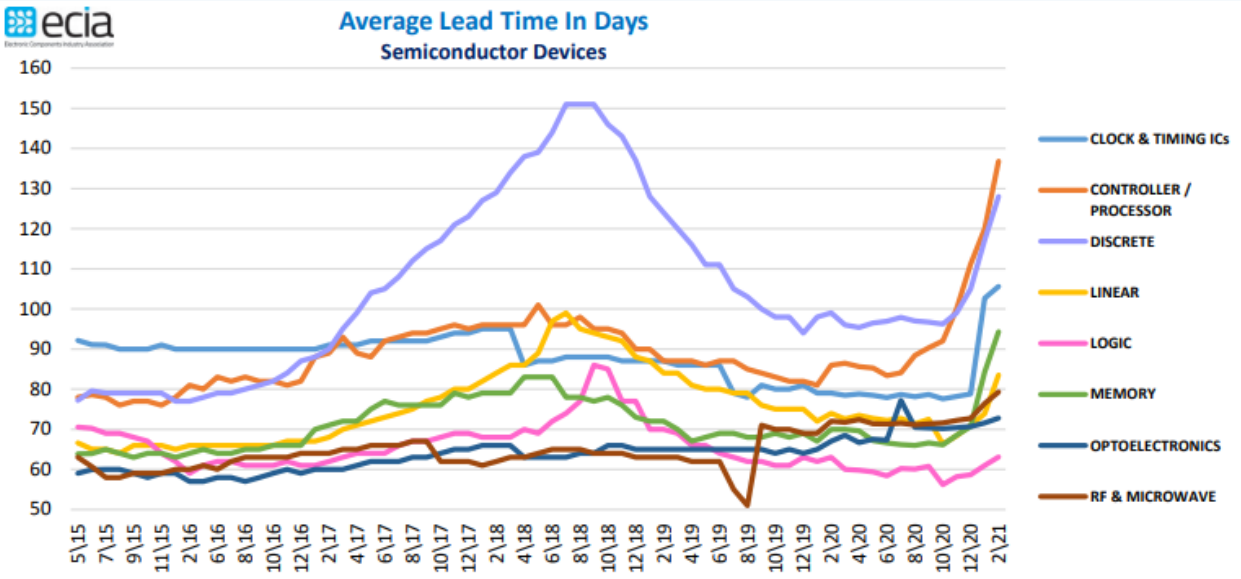
Average lead time for various types of semiconductors, source: ECIA
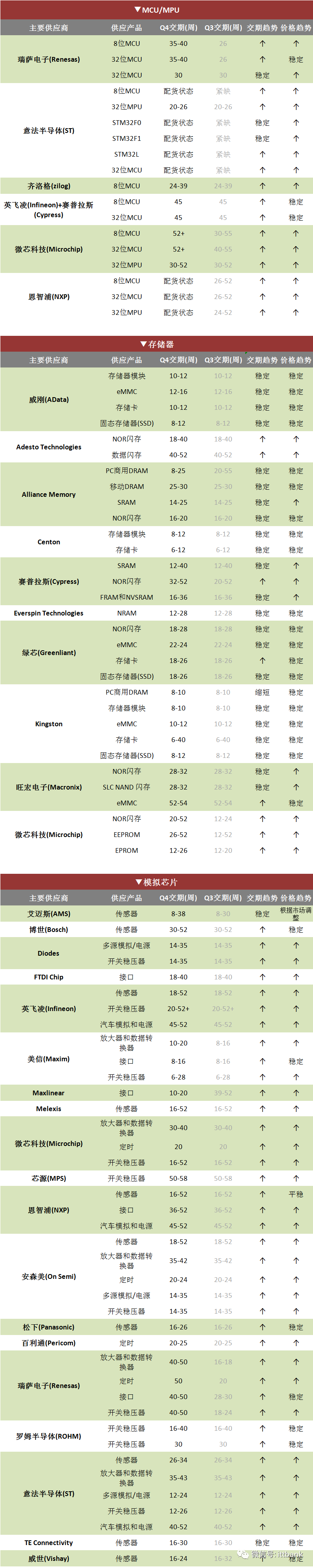
Various chip delivery schedules in the fourth quarter of 2021, source: ittbank
Supply side: 12-inch capacity increases more, 8-inch will be insufficient for a long time
Different from the previous round of global wafer production shortage in 2017-2018, this round of shortages shows a shortage of production capacity across the board.
The first is the long-term shortage of 5nm-7nm production capacity. Due to the high technical difficulty and high R&D costs, the advanced process is gradually monopolized by a few fabs. Currently, only [敏感词] and Samsung are competing in the 7nm and below process.
Advanced process foundry has become a seller's market. Driven by the demand for high-performance computing, Apple, Qualcomm, AMD, NVIDIA and others will divide up new production capacity of more advanced processes, such as CPUs and GPUs of PCs, servers, and game consoles. , the explosion of demand for mining machine ASIC chips, etc., are the key drivers for the shortage of 5nm-7nm production capacity.
The shortage of 10nm-20nm production capacity has been partially alleviated. 14nm is mainly used to produce 4G mobile phone processors, server chips, set-top box chips, security chips, Internet of Things SOC, etc. According to IC insights data, 10-20nm production capacity accounts for 38.4%, which is the largest proportion in the production capacity of each process. In the future, with the increase of 5G penetration rate, the demand for 4G mobile phones will also decline, and the shortage of production capacity of this process will be further alleviated.
The 40-65nm process has maintained a tight balance between supply and demand for a long time, and the demand explosion and extrusion effect have exacerbated the shortage of production capacity. The demand for the 40-65nm process is strong, and the downstream includes many downstream markets such as automotive MCU, CIS, IOT communication chips, NorFlash, etc., and has maintained a tight balance between supply and demand for a long time. Once a certain market demand breaks out rapidly, it is easy to squeeze the overall production capacity and cause shortages. goods. In the past 21 years, in order to alleviate the serious shortage of automobiles, [敏感词] has inserted orders to produce automobile chips in the form of super urgent orders, and transferred some production capacity of touch panel driver IC and CIS, which has caused CIS, WiFi Bluetooth chips, Norflash, etc. to be more urgent.
In addition, in the past two years, the capacity utilization rate of 8-inch mainstream fabs has been maintained at more than 90% for a long time. With the rapid outbreak of downstream demand since the second half of 2020, the production capacity is far from meeting the supply. For a long time, the expansion of 8-inch wafers has been relatively small, and the average compound growth rate from 2016 to 2019 is 3.7%. And because many 6-inch and below fabs have been closed or rebuilt, the burden of 8-inch wafer capacity has increased. On the one hand, due to the larger area of 12-inch wafers compared to 8-inch wafers, the more chips that can be cut with a moderate increase in material and process costs, the cost of chips can be reduced by more than 40%. On the other hand, 12-inch fabs are more efficient to invest in. To build a 50,000-piece/month production line, the equipment investment required for a 130nm 8-inch production line is about $1.4 billion, while the investment for a 90nm 12-inch production line is about $2.1 billion. Therefore, under the equivalent 8-inch capacity scale, 90nm 12-inch production Compared with the 130nm 8-inch production line, the investment is less. The fab is more motivated to build a 12-inch production line.
As fabs gradually upgrade to 12 inches, equipment suppliers are no longer supplying new 8-inch equipment. New or expanded 8-inch fabs can only be expanded by purchasing second-hand equipment. Used equipment supplier SurplusGlobal said the industry needs 2,000-3,000 new or refurbished 8-inch equipment to meet 8-inch fab demand, but fewer than 500 8-inch equipment are available. From the perspective of the global TOP10 wafer foundry production capacity, after 2017, including 12 inches, the production capacity of TOP10 manufacturers has basically maintained a small increase. In addition, even if the 8-inch production line is currently expanding, it will take 2-3 years to build, making it difficult to meet production capacity requirements in the short term.
According to IC Insights data, since 2009, the number of fabs closed or rebuilt has reached as high as 100, of which 25 are 8-inch, but more are 6-inch and 4-inch fabs, the number is as high as 64. The shutdown of the 6-inch wafer production line has shifted demand to 8-inch wafers, further increasing the pressure on 8-inch wafer production capacity.
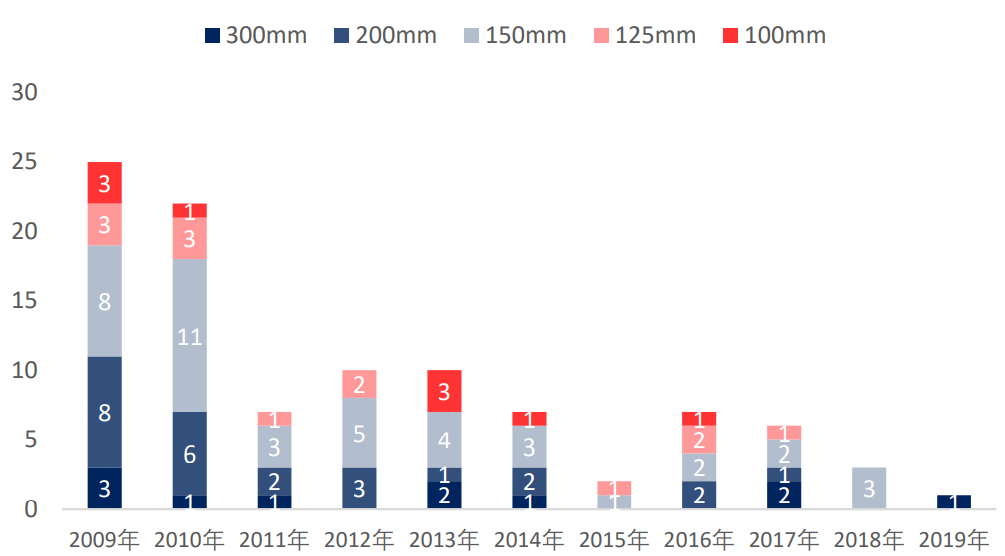
Number of fab closures since 2009 (home), source: ICInsights
Although major fabs have begun to expand their production capacity, far water cannot save near fire. From the expansion of production to the launch of real wafers, there are at least two to three years of cycle, so from the perspective of the supply side, the short-term capacity shortage cannot be alleviated.
Demand side: consumer demand declined in Q4, cars and servers were still hot
From the demand side, the auto industry, which is the most out of stock this year, will ease, but the long-term tension will continue. The shortage of automotive MCUs is the main reason for the cliff-like shortage of automobiles. Currently, about 70% of the world's automotive MCUs are produced by [敏感词], and top suppliers are highly dependent on [敏感词]. In the first half of 2020, due to the poor sales of automobiles affected by the epidemic, OEMs followed the JIT business model and cut orders sharply. In the second half of the year, car sales rebounded more than expected, and OEMs restarted pulling goods. However, due to the difficulty of rapid recovery of supply, it was far from meeting market demand.
However, from the first quarter, [敏感词] will insert orders to produce automotive chips in a super urgent order. The serious shortage of automotive cores may gradually ease, but in the long run, power devices such as automotive MCUs and IGBTs will still maintain a tight balance between supply and demand.
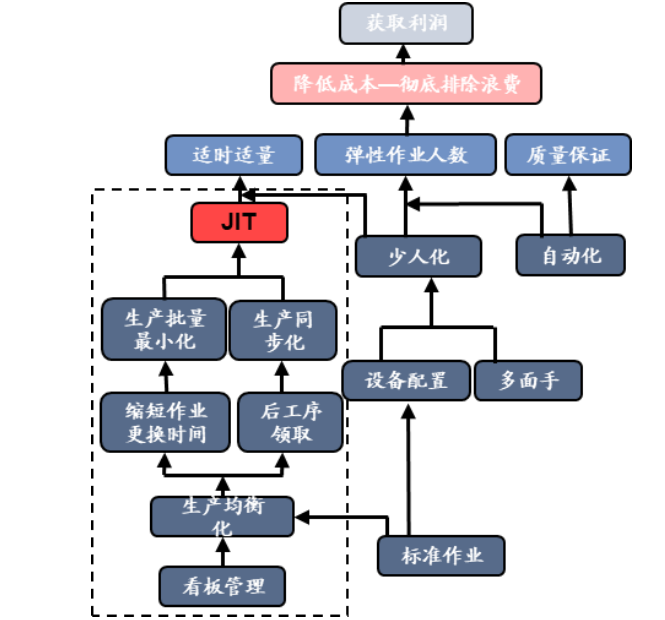
The automobile and industrial markets generally follow the JIT (just-in-time) production model. Source: MBA Think Tank Encyclopedia
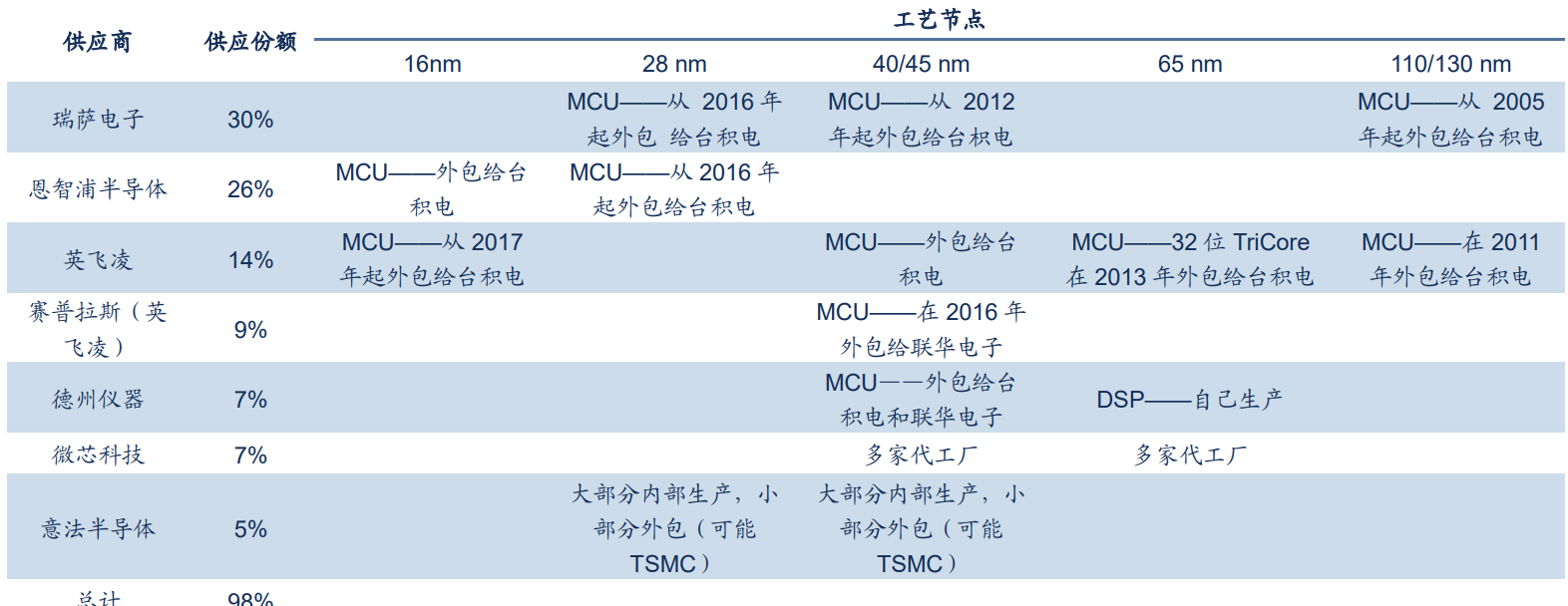
Automotive MCU suppliers and their reliance on [敏感词], source: IHS markit
Smartphones are affected by the epidemic and China's top technology enterprise incidents in 2020, and major mobile phone manufacturers have increased their stocking efforts. However, due to the insufficient preparation of SOC suppliers, mobile phone shipments still fell short of expectations. Entering 2021, the supply of mid-to-low-end models will improve rapidly, and the chips that are still out of stock mainly include flagship chip, CIS, and power supply chips. According to Cinda Electronics Industry Chain Research, the OEM yield rate of the flagship processor Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 at Samsung is less than 50%; the early Texas Blizzard also affected the production of Qualcomm RF Transceiver and Samsung CIS at Samsung's Texas factory; in addition, fast charging The strong demand has led to a significant increase in the number of power supply chips related to mobile phone Chargers.
Compared with mobile phones, the demand for "home economy" such as PCs and tablet computers has increased in volume. The market generally believes that the explosive demand for PCs and tablet computers is mainly catalyzed by the epidemic, and people's lifestyles and production methods have changed after the epidemic. Coupled with the demand for gaming computers and notebooks driven by the digital currency frenzy. In Q1 2021, global PC shipments reached 83.98 million units, a year-on-year increase of 55.2%. The emergence of concepts such as online office and metaverse will further contribute to the growth of the server market.
From the perspective of the downstream demand structure of the semiconductor industry, according to IC Insights data, computers, communications, and consumption are the top three downstream markets, accounting for 35.6%, 35.6%, and 11.8% respectively in 2019. With the development of automotive electronics, the proportion of the automotive market has continued to increase, from 4.7% in 1998 to 8.7% in 2019. Looking forward to 2024, the share of the automotive market will further increase to 9.7%, highlighting the high growth of automotive electronics. The computer, communication, industrial and other markets will also usher in the transformation of the application structure. Emerging applications such as 5G will also promote the continuous growth of global semiconductors for a long time.
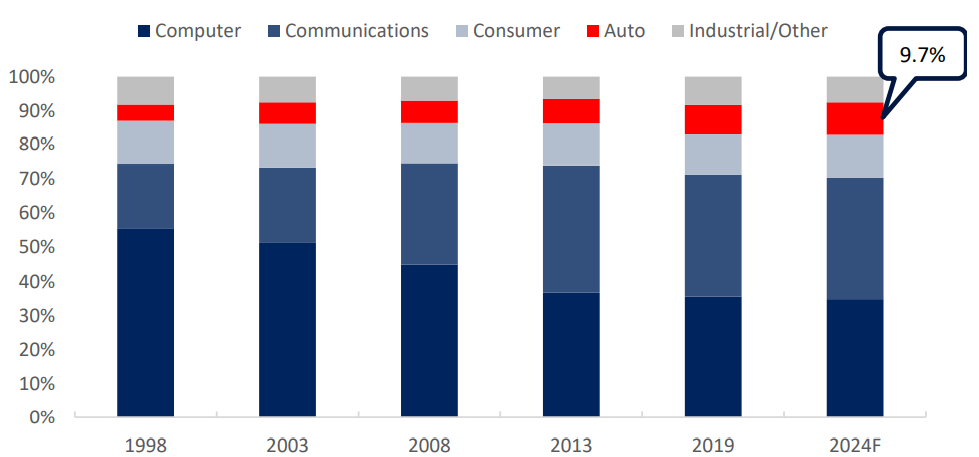
1998-2024F Semiconductor segment downstream market share, source: ICInsights
Channel side: the risk of "roasted seeds and nuts" of components
In analyzing the price increase and shortage of components, there is a view that the "roasting and hoarding" behavior of local component channel dealers in China has magnified the shortage of goods in the market.
The author has different opinions on this. The author thinks that the limitation of out-of-stocks mainly comes from upstream foundries, because the production capacity has been fixed, and no matter how much channel providers do their best, there is no way to conjure wafers out of thin air.
In the entire semiconductor industry chain, channel providers are relatively the weakest. "What is the best state of the game? That is, we can both fight and talk, and no one can eat anyone. This is the best state." Shenzhen Jinhangbiao Electronics Co., Ltd. and Shenzhen Sako Micro Semiconductor Co., Ltd. Manager Song Shiqiang believes that channel dealers do not have any capital to compete with original factories and fabs. Under the current situation of the seller's market, channel dealers and small and medium-sized customers can only passively accept the price passed down from upstream.

Huaqiangbei Electronic Person Song Shiqiang
The original factory executive said in the circle of friends that he would jump off the building, we can certainly regard it as a joke. But in the tide of shortages and price hikes this year, the ones who really want to jump off the building may be the downstream end customers. Because of the wave after wave of price increases, they have gradually drained their last traces of flesh and blood. Some channel dealers posted pictures in the circle of friends, saying that the upstream price increase pressure is passed on, and it is the channel dealers and end customers who ultimately pay the bill.

It can be said that the small and medium-sized channel dealers can survive, thanks to the low degree of standardization of components, because there are millions of material numbers, which gives Huaqiangbei's channel dealers a living space, but the gross profit is very low. Song Shiqiang wrote a lot of stories about Huaqiangbei's "get rich overnight" in his public account this year, but he also said that behind the rapid wealth, there are more extremely low gross profits and the real risk of "jumping off the building".
He concluded that the basis of component roasting comes from the compatibility of the semiconductor supply chain, that is, out of 2,000 materials, as long as 100 materials are out of stock, the terminal will not be able to ship. If you can predict in advance which 100 materials will be in short supply, there will be room for speculation. However, in practice, this judgment is entirely based on experience, and it is difficult to evaluate if one has not been deeply involved in a certain field for many years and has a basic judgment on the needs of upstream and downstream. He said that the current roasted seeds and nuts are more based on rapid adjustment and feedback based on market price fluctuations, and the cycle is very short, so the profit is actually not as high as imagined.
Finally, Song Shiqiang believes that this year's price hike has overdrafted the financial costs of downstream customers, and many factories have not yet digested their inventories. Therefore, the current market demand gradually weakened in Q4.
Review: To jump or not to jump, that is the question
On the one hand, the market demand has turned weak, and on the other hand, the upstream wafer production capacity continues to be in short supply. The contradiction between the two actually reflects the time difference between upstream and downstream demand transmission. Once the inventory risk is not well grasped, it will not only be the upstream original factory that jumps off the building.
Looking forward to 2022, the risk of inventory water level has been mentioned by more and more industry insiders, and there are many voices questioning the high inventory level.
In fact, by Q4 2021, most of the part numbers on the market are no longer in short supply. Referring to historical experience, the upward phase of inventory replenishment in the new cycle generally lasts for about 4-5 quarters.
Recently, Wang Minwen, chairman of Leon Micro, said in an exclusive interview with the media that from the perspective of supply and demand, this round of business cycle may last until the second half of 2023. In addition, the domestic semiconductor wafer industry may enter two or three years later. to a stage of mergers and acquisitions.
The industry is still in the inventory replenishment stage. Inventory cycles occur due to the misalignment and time lag between changes in market demand and fab production. Judging from the inventory level of the most representative semiconductor design leading companies, the general semiconductor inventory cycle is about 2-3 years. Since 2Q18, the industry has been in the destocking stage. In 3Q19, the industry inventory has reached the bottom, and the industry has ushered in a short-term replenishment stage. However, due to the sudden impact of the new crown epidemic, the industry chain has unclear judgment on future demand, and some areas have started inventory adjustments. However, since the third quarter of 2020, the epidemic has dissipated, demand has recovered, and the industry has restarted to replenish inventories. Although the current inventory level has risen, the turnover days are still declining.
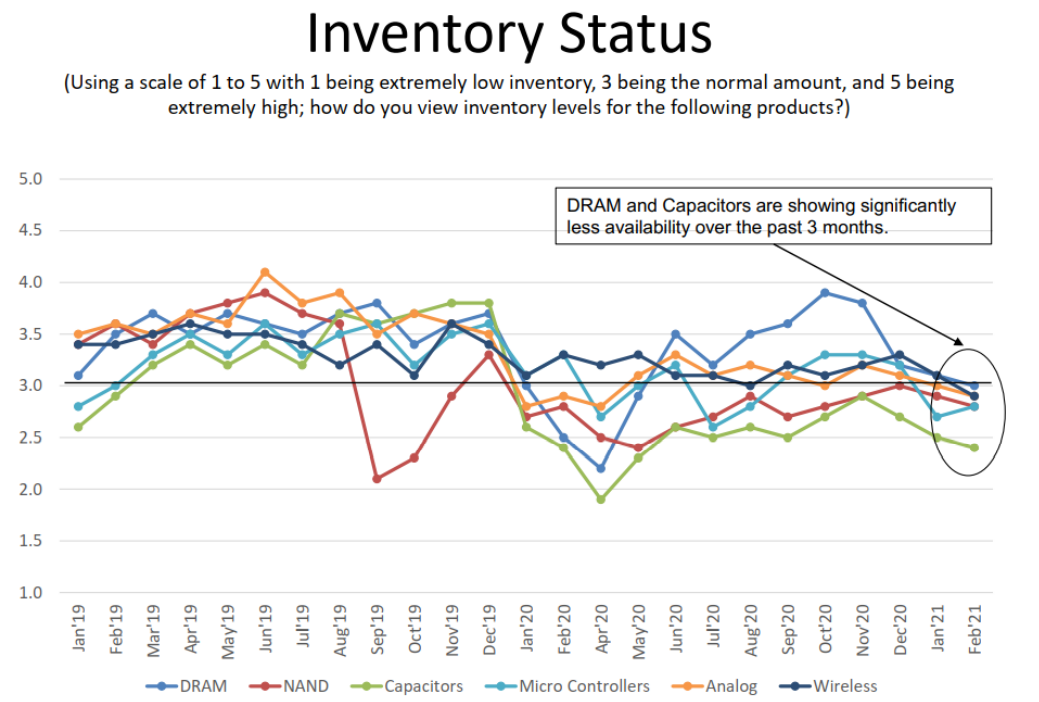
List of current inventory levels of various electronic components, source: TPC
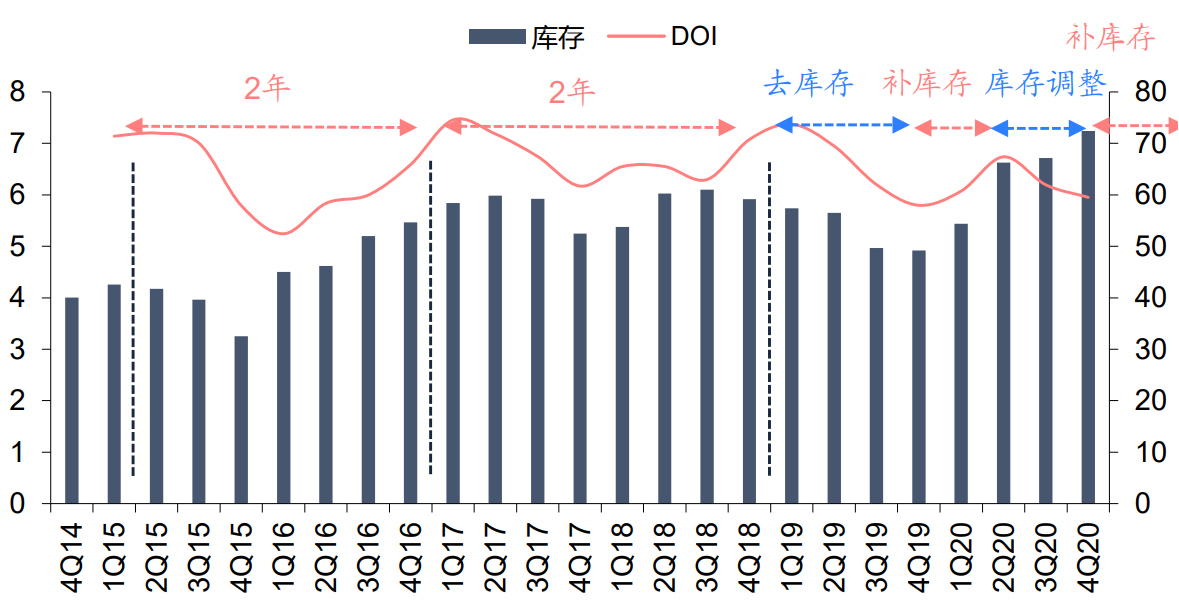
Overseas semiconductor design leading inventory cycle (billion US dollars, right axis (days)), source: Bloomberg
From the perspective of product demand, 5G mobile phones will gradually peak, but with the development of vehicle electrification, intelligence, and the Internet of Things, the product cycle is still going up.
From the perspective of capacity release, major fabs have expanded their production in the second half of 2020, and it is expected to gradually release capacity by 2022/2023. Song Shiqiang believes that the production capacity release cycle of the fab may be longer, and it will take three years. "It takes two years to build a factory and adjust the machine testing equipment. If I can do a good job in personnel and connect with downstream customers in these two years, it will take three years. Maybe the downstream packaging and testing cycle will be better. , it is estimated that it is also two years.”
The author believes that the current round of shortages and price increases in the semiconductor industry is driven by many factors, not only the black swan factor of the epidemic, and the inventory cycle. What should be paid more attention is that a new round of 5G, AIOT, automotive electronics, etc. is currently ushering in. As demand explodes, the semiconductor market will usher in a 5-10-year demand cycle.
But it is worth noting that if domestic chips cannot use the tide of shortage to strengthen their internal strength, once the tide of shortage passes. Customers who are forced to replace domestic products may return to European and American chips. Liked and forwarded more than 100 times, the author will launch an analysis of the difficulties, opportunities and challenges in the replacement of domestic chips.
Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from "Non-Fei Observation". This article only represents the author's personal views, not the views of Sacco and the industry. It is only for reprinting and sharing, and supports the protection of intellectual property rights. Please indicate the original source and author for reprinting, if any Infringement please contact us to delete.



Site Map | 萨科微 | 金航标 | Slkor | Kinghelm
RU | FR | DE | IT | ES | PT | JA | KO | AR | TR | TH | MS | VI | MG | FA | ZH-TW | HR | BG | SD| GD | SN | SM | PS | LB | KY | KU | HAW | CO | AM | UZ | TG | SU | ST | ML | KK | NY | ZU | YO | TE | TA | SO| PA| NE | MN | MI | LA | LO | KM | KN
| JW | IG | HMN | HA | EO | CEB | BS | BN | UR | HT | KA | EU | AZ | HY | YI |MK | IS | BE | CY | GA | SW | SV | AF | FA | TR | TH | MT | HU | GL | ET | NL | DA | CS | FI | EL | HI | NO | PL | RO | CA | TL | IW | LV | ID | LT | SR | SQ | SL | UK
Copyright ©2015-2025 Shenzhen Slkor Micro Semicon Co., Ltd